
Baron Dhanis, Belgian gunboat converted from Lake Tanganyika
Some diparate countries will be studied here: It should not be forgotten that many European nations were created or resurrected (outside of Belgium) at the end of the war with the fall of the great empires: In Europe especially, Yugoslavia, Poland, the three Baltic States, Estonia, Lithuania, Latvia, Yugoslavia, and Albania. For the rest, Haiti, the French-speaking Black Republic of Hispaniolia, neighbor of St Dominic had to ensure its defense by some valuable units, Cambodia, French protectorate just like Morocco, Persia and Egypt, recovering territories after the fall of the Ottoman Empire.
 The Belgian Navy:
The Belgian Navy:
In 1914 the Belgian Naval Force did not include any squadron of the high seas but a handful of rapid gunshields employed by the government and often unarmed (a dozen will be at the beginning of hostilities), and the old City of Antwerp ( 1864), the only specialized fishery guard. On Lake Tanganyika, during the war, she will also have the torpedo boat at Spar Netta (1915), a patrol boat on Lake Kiru, the gunboat Paul Renkin who operated in the Congo, and the torpedo boat Vankerhoven on the Nile. It was not until the occupation of flanders by the Germans and the establishment of efficient and well-protected naval bases that the government became aware of the usefulness of a small coastal naval force, which it developed at from 1919 thanks to allies with disparate ships.
 The Cambodian Navy:
The Cambodian Navy:
Protectorate French since 1863, she defended with a semblance of navy constituted by the old gunboat Lutin dating from 1874 and also used as a royal yacht, and two other gunboats (civilian steam of 80 tons), armed with a single light gun as well as three other armed vapors assisted by about thirty armed junks. In case of attempted invasion, France had a squadron on site.
The Cuban Navy:
Since its independence in 1898, this ancient “Pearl of the Spanish Empire”, had the economic resources to build a force as important as that of Haiti, not far from there, but not the necessary, because a few cables, the US Navy could intervene on what was then its “preserve”, and did not stop doing it… eight times. The port of Havana had become an annex naval base of the US Navy.
In 1911, was launched at the Cramp Yards a 2000 tons sloop, naturally called Cuba and another small gunboat ordered at the same time, the Patria. The Cuban government also ordered the two small gunboats of the Diez de Octubre class at the same site, and built two 80 ton wooden steamers locally (Habana and Pinar del Rio in 1912). These were added to the 8 small steamers (less than 50 tons) used as a guard fishery.
In 1917, Cuban neutrality shifted, always in the bosom of the big neighbor, into an open hostility with Germany. This enabled him to seize in his ports four large German steamers of more than 19 000 GRT, quickly entrusted to the good care of Uncle Sam. The Caribbean sector, with a fairly large traffic, was not directly involved in the England and the U-Bootes did not come to venture there, however, the Cuban gunboats patrolled there in agreement with the US Navy. Four wooden submarine hunters of the “110 feet” type were allocated to his “fleet” in 1918.
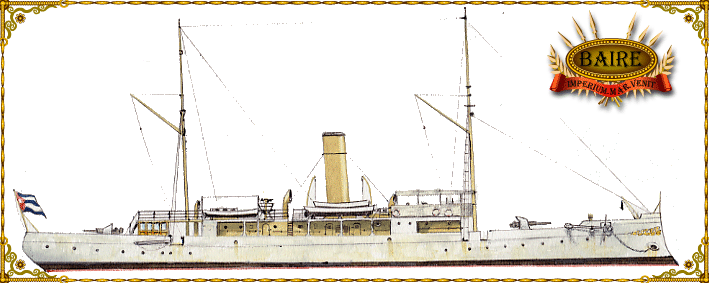
The Baire in 1914, its peacetime livery.
The Baire was at the beginning of the century, the only ship of importance in the Cuban “fleet”, which also had only a few peach guards. The Baire was paradoxically built in Germany, in Schichau, launched in 1906, and served until late in the years 35-36.
Displacement (1908): Displacement & Dimensions 500t; 59.74 x 7 x 2.74m
Propulsion 1 propeller, 1 mach. vap. Babcock boiler, 1200 hp. and 14 knots max.
Armament 2 x 57 mm, 2 x 47 mm guns.
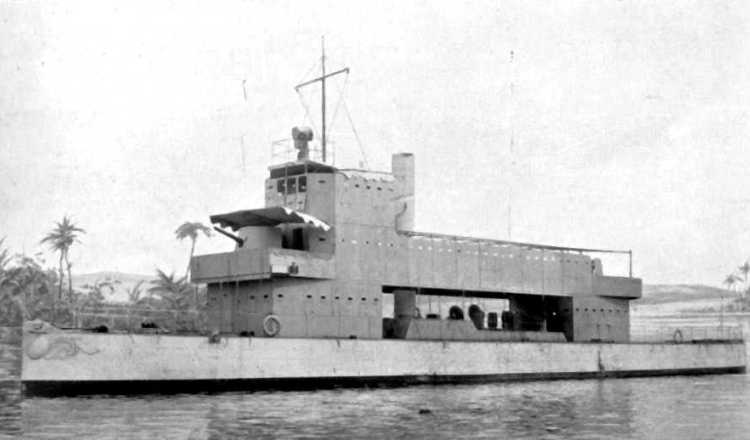

Egyptian gunboat Melik
 The Egyptian Navy:
The Egyptian Navy:
Apart from some old yachts of armed servitude on the nile (Dahabieh in particular), the “flotilla” of caliph Ismail I included only three gunboats dating from 1863 to 1865. From 1882, the British seized the Egypt to control the Suez Canal, although the country remained under Ottoman jurisdiction. The effective control of the British made Egypt officially warring against the central empires. his fleet was not a necessity in view of the forces deployed locally by the triple agreement. Numbers: Gunboats Karthoum, Dongola and Jeafferieh (1862-65), retired from service at the end of 1914, 6 coastguards, Noor el Bahr, Nesim, Marda, Zarif, Saria and Abbas, dating from 1884 to 1891. The last was torpedoed by the U35 in Bay of Solloum in Nov. 1915. Armed Yachts Mahroussa, Emirighain, and Abdul Monaym (1865-1902). There were also 10 gunboats on the Nile, 4 of the Tamai class (1884), 3 of the El Zafir class (1896) and 3 of the Sultan class (1896).

Crete a pierot, Haitian gunboat.
 The Haitian Navy:
The Haitian Navy:
A highly indebted country, he built himself a relatively powerful navy for his low income, and his buildings had the opportunity to fight against his debtors, especially Germans. In 1903, for example, the gunboat Panther sank as a result of a commitment Crete to Pierot. In 1914, Haiti was neutral and was not interested in anyone. His forces included a cruiser, the ex-Umbria Ferrier, acquired in 1911 from Italy, but the latter sank in 1913 due to the inexperience of his crew. She had 4 gunboats, Dessalines (1883), Toussaint-Louverture (1886), and 2 Capois Death (1893). In 1915, US Marines landed in Haiti when the lack of funds government disintegrated and it was chaos. The latter remained there until 1934. All gunboats were sold to scrap metal and the Haitian navy disappeared. This did not prevent the new government under guardianship from declaring war on Germany in July 1918.

Rare photo of Persian Persepolis gunboat 1886 (hippostcard.com)
 The Persian navy:
The Persian navy:
In 1886 the Persepolis gunboat was acquired as was the German Susa river patrol boat, constituting the nucleus of a naval force. Due to the lack of competent local personnel, German sailors and officers employed them. But lack of maintenance funds the ships were neglected and were quickly in poor condition. The crews returned to France and the ships rotted at the dock, a fate comparable to the Turkish navy. Muzaffer gunboat and the Royal Selika yacht were added in 1899. The Persians remained neutral, but their ships were occasionally used by the Royal Navy in the Indian Ocean.

 Latest Facebook Entry -
Latest Facebook Entry -  X(Tweeter) Naval Encyclopedia's deck archive
X(Tweeter) Naval Encyclopedia's deck archive Instagram (@navalencyc)
Instagram (@navalencyc)





 Austrian Navy
Austrian Navy French Navy
French Navy Royal Navy
Royal Navy Armada Espanola
Armada Espanola K.u.K. Kriegsmarine
K.u.K. Kriegsmarine Dansk Marine
Dansk Marine Nautiko Hellenon
Nautiko Hellenon Koninklije Marine 1870
Koninklije Marine 1870 Marinha do Brasil
Marinha do Brasil Osmanlı Donanması
Osmanlı Donanması Marina Do Peru
Marina Do Peru Marinha do Portugal
Marinha do Portugal Regia Marina 1870
Regia Marina 1870 Nihhon Kaigun 1870
Nihhon Kaigun 1870 Preußische Marine 1870
Preußische Marine 1870 Russkiy Flot 1870
Russkiy Flot 1870 Svenska marinen
Svenska marinen Søværnet
Søværnet Union Navy
Union Navy Confederate Navy
Confederate Navy Armada de Argentina
Armada de Argentina Imperial Chinese Navy
Imperial Chinese Navy Marinha do Portugal
Marinha do Portugal Mexico
Mexico Kaiserliche Marine
Kaiserliche Marine 1898 US Navy
1898 US Navy Russkiy Flot
Russkiy Flot French Naval Aviation
French Naval Aviation Russian Naval Aviation
Russian Naval Aviation Sovietskiy Flot
Sovietskiy Flot Royal Canadian Navy
Royal Canadian Navy Royal Australian Navy
Royal Australian Navy RNZN Fleet
RNZN Fleet Chinese Navy 1937
Chinese Navy 1937 Kriegsmarine
Kriegsmarine Chilean Navy
Chilean Navy Danish Navy
Danish Navy Finnish Navy
Finnish Navy Hellenic Navy
Hellenic Navy Polish Navy
Polish Navy Romanian Navy
Romanian Navy Turkish Navy
Turkish Navy Royal Yugoslav Navy
Royal Yugoslav Navy Royal Thai Navy
Royal Thai Navy Minor Navies
Minor Navies Albania
Albania Austria
Austria Belgium
Belgium Columbia
Columbia Costa Rica
Costa Rica Cuba
Cuba Czechoslovakia
Czechoslovakia Dominican Republic
Dominican Republic Haiti
Haiti Hungary
Hungary Honduras
Honduras Estonia
Estonia Iceland
Iceland Eire
Eire Equador
Equador Iran
Iran Iraq
Iraq Latvia
Latvia Liberia
Liberia Lithuania
Lithuania Mandchukuo
Mandchukuo Morocco
Morocco Nicaragua
Nicaragua Persia
Persia San Salvador
San Salvador Sarawak
Sarawak Uruguay
Uruguay Venezuela
Venezuela Zanzibar
Zanzibar Warsaw Pact Navies
Warsaw Pact Navies Bulgaria
Bulgaria Hungary
Hungary

 Bundesmarine
Bundesmarine Dutch Navy
Dutch Navy Hellenic Navy
Hellenic Navy Marina Militare
Marina Militare Taiwanese Navy
Taiwanese Navy Chinese Navy
Chinese Navy Indian Navy
Indian Navy Indonesian Navy
Indonesian Navy JMSDF
JMSDF North Korean Navy
North Korean Navy Philippines Navy
Philippines Navy ROKN
ROKN IDF Navy
IDF Navy Royal New Zealand Navy
Royal New Zealand Navy Egyptian Navy
Egyptian Navy South African Navy
South African Navy

































 RN
RN
 Marine Nationale
Marine Nationale
 Soviet Navy
Soviet Navy
 dbodesign
dbodesign